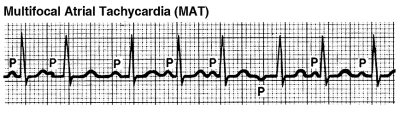
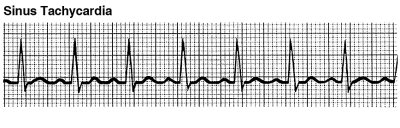
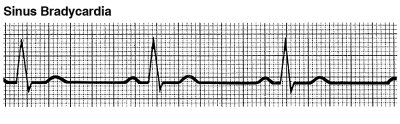
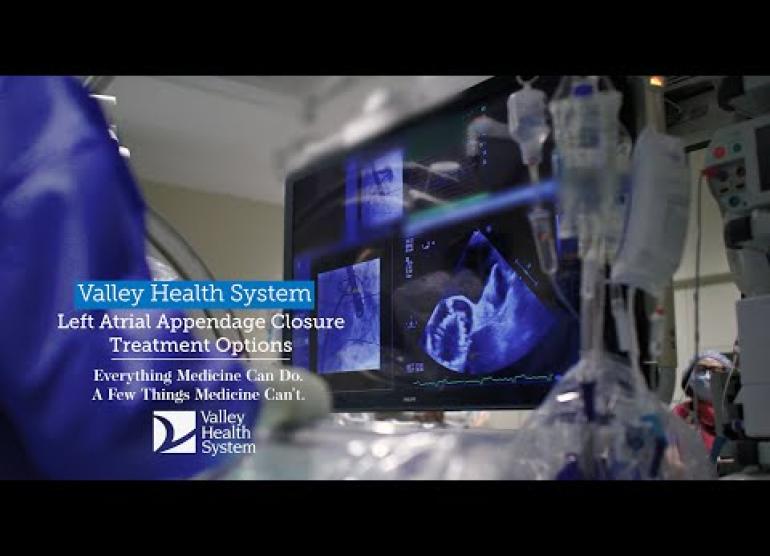
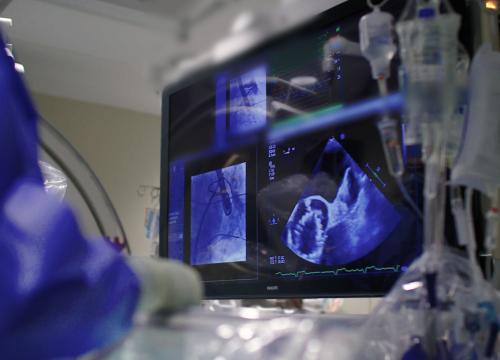
An arrhythmia is an irregular heart rhythm. Arrhythmias occur when the electrical impulses that control your heartbeat don’t work properly. This causes your heart rhythm to be too slow, too fast or unpredictable.
If you have an arrhythmia, you may have symptoms like palpitations and fainting (syncope). Some types of irregular heart rhythms like atrial fibrillation (AFib) can also raise your risk for stroke and heart failure.
At Valley, our electrophysiology team specializes in identifying all types of arrhythmias. We can also restore your normal heart rhythm using the latest treatments that you won’t find at most hospitals.
Arrhythmia Symptoms
Symptoms of arrhythmias include:
- Pounding or fluttering sensations in the chest (palpitations)
- Lightheadedness
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fainting (syncope)
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Sweating
You don’t have to suffer with the discomfort and uncertainty of arrhythmia symptoms. Our electrophysiologists can help determine the cause and recommend treatment — helping you feel better and avoid other health risks.
Types of Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias can start in the upper chambers (atria) or the lower chambers (ventricles) of your heart. Valley’s electrophysiologists specialize in treating all types of irregular heart rhythms, including the most complex. Some of the arrhythmias we identify and treat include:
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is the most common arrhythmia. AFib causes the upper two chambers of your heart (atria) to quiver, which makes your heart beat quickly and erratically.
If your AFib is not under control, it can raise your risk for stroke, heart failure and other health problems. Valley offers the latest treatments for AFib and other arrhythmias through the Snyder Center for Comprehensive Atrial Fibrillation.
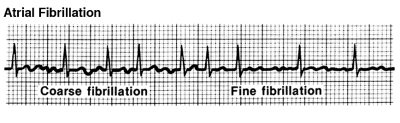
Atrial Flutter
Like AFib, atrial flutter begins in your heart’s upper chambers. However, atrial flutter is less erratic than AFib. Still, it can raise your risk for stroke, so it requires treatment.
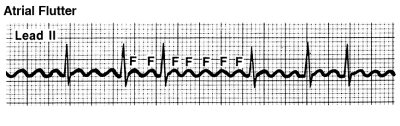
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT)
PSVTs are episodes of a very rapid heartbeat that starts and stops suddenly. This type of arrhythmia usually begins in your heart’s upper chambers.
Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs) and Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)
PACs and PVCs may make you feel like your heart skipped a beat. They are usually harmless and don’t require treatment unless they bother you.
Ventricular Fibrillation (VFib)
VFib is a dangerous heart rhythm that requires emergency treatment. During VFib, the lower chambers of your heart quiver so your heart cannot pump blood properly. Delivering an electric “shock” to your heart can help restore the rhythm back to normal.
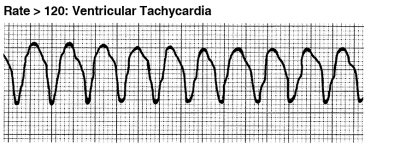
Ventricular Tachycardia (VTach)
This rapid heartbeat also begins in the lower chambers of your heart. Because your heart is beating so fast, it pumps less blood throughout the body.
VTach also requires emergency treatment with an electric “shock” to your heart to return your heart rhythm back to normal.
AV Nodal Re-Entrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)
AVNRT is a common type of rapid heartbeat that occurs when your heart has more than one electrical pathway. AVNRT is not usually life-threatening, but treatment can improve symptoms like chest pain and dizziness.
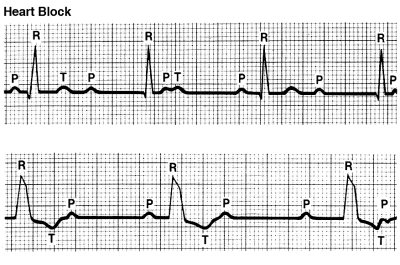
Heart Block (Atrioventricular Block)
A heart block occurs when the electrical signal in your heart gets delayed or blocked. Not all types of heart blocks are serious. But without treatment, some can lead to bradyarrhythmia (irregularly slow heartbeat) and even cardiac arrest (when your heart stops beating).
Arrhythmia Diagnosis at Valley
Getting an accurate arrhythmia diagnosis ensures you receive the best possible treatment for your arrhythmia.
After we take your medical history, we may recommend some tests to determine the cause of your symptoms. These may include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG), a noninvasive test to evaluate the electrical activity in your heart
- Echocardiogram, a noninvasive test that uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to show the size, structure and motion of your heart
- Chest X-ray, which shows the size of your heart
- Exercise stress testing, which checks many aspects of your heart function while you are on a treadmill or stationary bike
- Ambulatory monitoring, which lets us track your heart rhythm at home. We offer all types of monitors, including portable Holter monitors and implantable loop recorders.
- Electrophysiology (EP) study, a minimally invasive procedure to find where the arrhythmia starts in your heart
- Tilt table testing, which allows us to recreate symptoms if you’ve had fainting spells (syncope) when you suddenly stand up. This helps us determine what’s causing you to faint.
Arrhythmia Treatment at Valley
Your arrhythmia treatment plan may include one or more options based on your overall health and your specific needs. These include:
- Lifestyle modifications
- Medications
- Procedures
- Cardiac device therapy
- Heart surgery
Lifestyle Modifications
Because heart disease causes many arrhythmias, we may recommend heart-healthy habits such as:
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a healthy diet
- Reducing stress
- Not smoking
- Limiting alcohol and caffeine
Medications
Your electrophysiologist may recommend certain medicines to help control your irregular heart rhythm and reduce your health risks. These may include:
- Antiarrhythmic medicines to steady an abnormal heart rhythm. Examples are sodium channel blockers, beta blockers, potassium channel blockers and calcium channel blockers. If you take these medications, we’ll carefully monitor you for side effects or signs that your arrhythmia is getting worse.
- Digoxin, a medication that can slow down heart rhythms and treat heart failure.
- Blood-thinners (anticoagulants) to help prevent blood clots. If you have AFib, these medicines can reduce your risk for stroke. Examples include warfarin, rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban.
We may also adjust your other medications, such as blood pressure medicines, that can affect your heart rate.
Procedures
We may recommend a procedure if we think it will help control your irregular heart rhythm. Procedures for arrhythmia include:
- Cardioversion, which uses an electrical shock to reset the heart rhythm back to normal
- Catheter ablation, which uses hot or cold energy to interrupt pathways in your heart causing your irregular heart rhythm
Cardiac Device Therapy
In some cases, your electrophysiologist may recommend an implantable device if other treatments do not control your irregular heart rhythm. Devices for arrhythmia include:
- A pacemaker to treat a slow heartbeat (bradycardia). This device sends low-energy electrical pulses to the heart if your heart rhythm slows or becomes erratic.
- An implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) to continuously monitor your heartbeat and deliver a lifesaving “shock” if your heartbeat becomes dangerously irregular.
- A left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) device, like the Watchman or Amulet, to reduce your stroke risk if you have AFib.
Heart Surgery
Most people with arrhythmias don’t need heart surgery. But if other treatments have failed to improve your arrhythmia, your electrophysiologist may recommend heart surgery.
If you have severe coronary artery disease and ventricular tachycardia, bypass surgery can improve blood supply to your heart.
Why Choose Valley for Arrhythmia Care?
- Convenient, timely care: We understand how frustrating it can be to wait to see a specialist for your heart. That’s why we aim to get you in to see our electrophysiologists within a week.
- An accurate diagnosis: Our team will make every effort to get the correct diagnosis for you, even if other centers haven’t. We won’t give up until we understand the cause of your arrhythmia symptoms — and have a plan to address your symptoms.
- AFib expertise: Through Valley’s Snyder Center for Comprehensive Atrial Fibrillation, we offer a team approach to treat AFib and other irregular heart rhythms. We will create a comprehensive plan that may include treatments you can’t find at most hospitals. For example, we offer the latest devices like Watchman and Amulet to reduce your risk for stroke. We also collaborate with other heart specialists at Valley on your care plan if you have AFib and heart failure.
- Local experts in ablation: You don’t need to travel to the city to find experts in catheter ablation for arrhythmias. Our team is skilled at performing complex ablations using a collaborative approach where two electrophysiologists work side by side. Our electrophysiologists are also studying the latest ablation techniques through clinical trials that are not available at many centers.